Introduction
Slip-On Flanges are a vital component in the world of industrial piping. They offer practical solutions for connecting pipes, making installations more efficient. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the world of Slip-On Flanges, exploring their features, applications, advantages, limitations, and FAQs.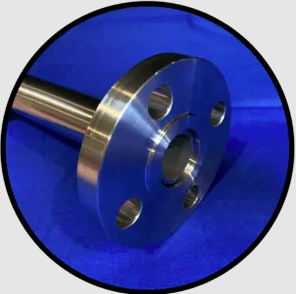
Image source:Texas Flange
Understanding Slip-On Flanges
Slip-On Flanges, also referred to as 'hubbed flanges,' along with some other styles, are designed to connect pipes. They feature a low-profile hub and are typically attached to a pipe using one or two fillet welds. The internal diameter of a Slip-On Flange's bore is larger than that of the connecting pipe, allowing it to slide or “slip” onto the pipe.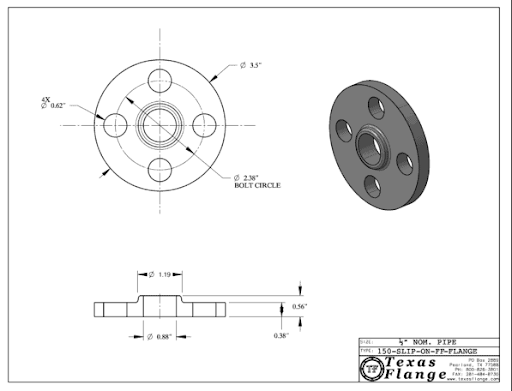
Image source:Texas Flange
Advantages of Slip-On Flanges
- 1.)Cost-Effective: Slip-On Flanges are cost-effective, making them a budget-friendly choice compared to Weld Necks.
- 2.)Ease of Installation: They require less skill for welding, have lower accuracy requirements for pipe cutting, and do not need weld preparation for the pipe end weld. The pipe fitter will thank you.
- 3.)Space Considerations: Ideal for situations where space limitations prevent the use of welding neck flanges which are butt welded and have a longer hub.
Limitations of Slip-On Flanges
- 1.)Reduced Mechanical Strength: Slip-On Flanges have reduced mechanical strength compared to welding neck flanges, limiting their suitability for some high-pressure applications.
- 2.)Unsuitable for Cyclic Loading: They are not recommended for applications involving cyclic loading.
- 3.)Non-Destructive Testing: Some non-destructive testing techniques on welds may be limited when using Slip-On Flanges.
- 4.)Size and Pressure Class Limitations: They may not be available in all sizes and pressure classes, so choosing the right flange is essential.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is a Slip-On Flange? A Slip-On Flange is a type of flange used for connecting pipes, featuring a low-profile hub and typically attached with one or two fillet welds. It derives its name from the fact that it “slips” on the pipe it is to be attached to.
- When should I use Slip-On Flanges? Slip-On Flanges are suitable for lower pressure applications and when space limitations prevent the use of welding neck flanges.
- What are the advantages of Slip-On Flanges? Advantages include cost-effectiveness, ease of installation, and suitability for projects with budget constraints.
- What are the limitations of Slip-On Flanges? Limitations include reduced mechanical strength, unsuitability for cyclic loading, and limitations in non-destructive testing.
- Do Slip-On Flanges come in various sizes? Yes, Slip-On Flanges are available in various sizes to accommodate different pipe dimensions.
- What materials are used for Slip-On Flanges? Materials include carbon steel, chrome alloys, stainless steel, aluminum, hastalloy, and more.
- Are there different classes of Slip-On Flanges? Yes, Slip-On Flanges come in various pressure classes, such as ANSI class 150, 300, and more.
- How are Slip-On Flanges installed? They are typically installed by welding one or two fillet welds to the pipe, providing a secure connection.
- Are Slip-On Flanges suitable for high-pressure applications? They are generally used in lower pressure applications. For high-pressure applications, welding neck flanges are often preferred.
- Can Slip-On Flanges be used with all pipe sizes? No, they may not be available in all sizes and pressure classes. It's essential to select the right flange for your specific piping requirements.